Levamisole Dosage Guide: Effective Use, Administration, and Important Safety Tips
May 14 2025Generic Drug Classifications: Understand How Medications Are Grouped and Why It Matters
When you pick up a generic drug classification, a system that groups medications by how they work in the body, their medical use, and their chemical structure. Also known as therapeutic categories, it helps doctors, pharmacists, and patients quickly understand what a pill does without memorizing brand names. You might not think about it, but every time you take a blood pressure pill, an antibiotic, or an antidepressant, you’re using a drug that fits into one of these categories. These groups aren’t just for experts—they’re your shortcut to knowing what to expect, what to watch out for, and how to compare options.
Take generic medications, pharmaceuticals that are chemically identical to brand-name drugs but sold under their active ingredient name. Also known as generic drugs, they make up over 90% of prescriptions in the U.S. because they’re cheaper and just as effective. But here’s the catch: two generics can belong to completely different classes. For example, lisinopril and amlodipine both treat high blood pressure, but one’s an ACE inhibitor and the other’s a calcium channel blocker. That matters because side effects, interactions, and who they work best for change based on class. If your doctor switches you from one generic to another, they might be switching classes—and that could mean a different side effect profile.
Drug classes don’t just help you understand prescriptions. They help you avoid dangerous mixes. Take drug classes, categories like NSAIDs, anticoagulants, or immunosuppressants that group drugs by their primary medical action. Also known as medication groups, they’re why you’re warned not to mix ibuprofen with blood thinners, or why you can’t take certain antibiotics with antacids. The posts below show real cases: how scopolamine interacts with sedatives, why antacids can hurt kidneys, and why missing a blood thinner dose is risky. All of these are tied to drug class behavior. Even the placebo effect with generics? That’s shaped by how people perceive the class—like thinking a blue pill for depression must work differently than a white one.
What you’ll find here isn’t a textbook list. It’s real-world stories from people who’ve navigated these classifications—whether they’re using cyclosporine for autoimmune disease, sildenafil for chronic pain, or albendazole to clear parasites. Some posts explain how cultural beliefs change how people take generics. Others show how switching from brand to generic isn’t always simple, even when the chemistry matches. You’ll see how diet affects hair loss meds, how probiotics help liver patients, and why a blood pressure drug like irbesartan might stop your migraines. These aren’t random. They’re all connected by the same idea: knowing the class tells you more than the name.
By the end, you’ll know why two pills that look nothing alike can be in the same group—and why that’s the key to safer, smarter, cheaper care. No jargon. No fluff. Just what you need to make sense of your meds.
 12 Nov
12 Nov
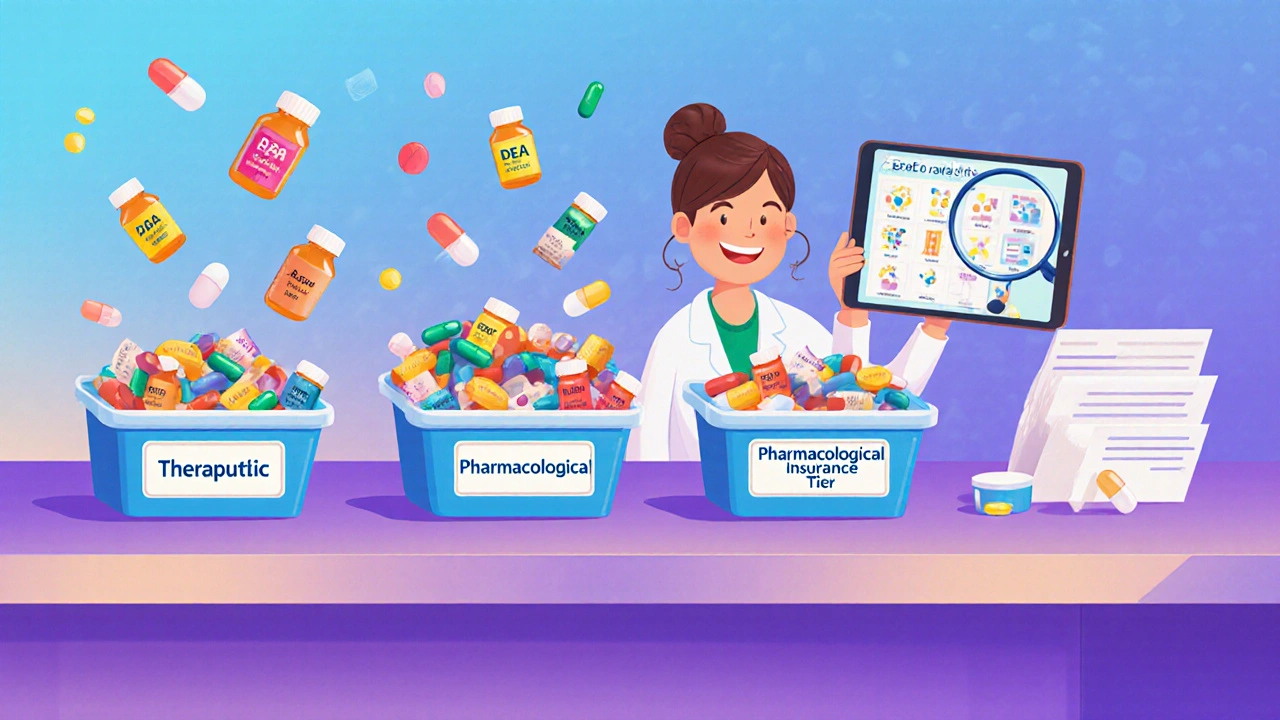
Generic Drug Classifications: Types and Categories Explained
Understand how generic drugs are classified by therapeutic use, mechanism of action, legal schedules, and insurance tiers. Learn why the same drug can be grouped differently-and how this affects your prescriptions and costs.
Read More...