OTC Sunscreens: How SPF, Broad Spectrum, and Reapplication Really Work
December 18 2025Audiometry Testing: What It Is, Why It Matters, and What to Expect
When you hear a sound but can’t quite make out the words, or if people seem to mumble more than usual, you might be dealing with audiometry testing, a clinical procedure used to measure how well a person can hear different sounds, pitches, and volumes. Also known as a hearing test, it’s the most reliable way to spot hearing loss before it affects your daily life. Unlike a quick check at a pharmacy, audiometry testing is done in a quiet room with calibrated equipment and interpreted by trained professionals. It’s not just for older adults—anyone exposed to loud noise, taking certain medications, or with a family history of hearing issues should get tested.
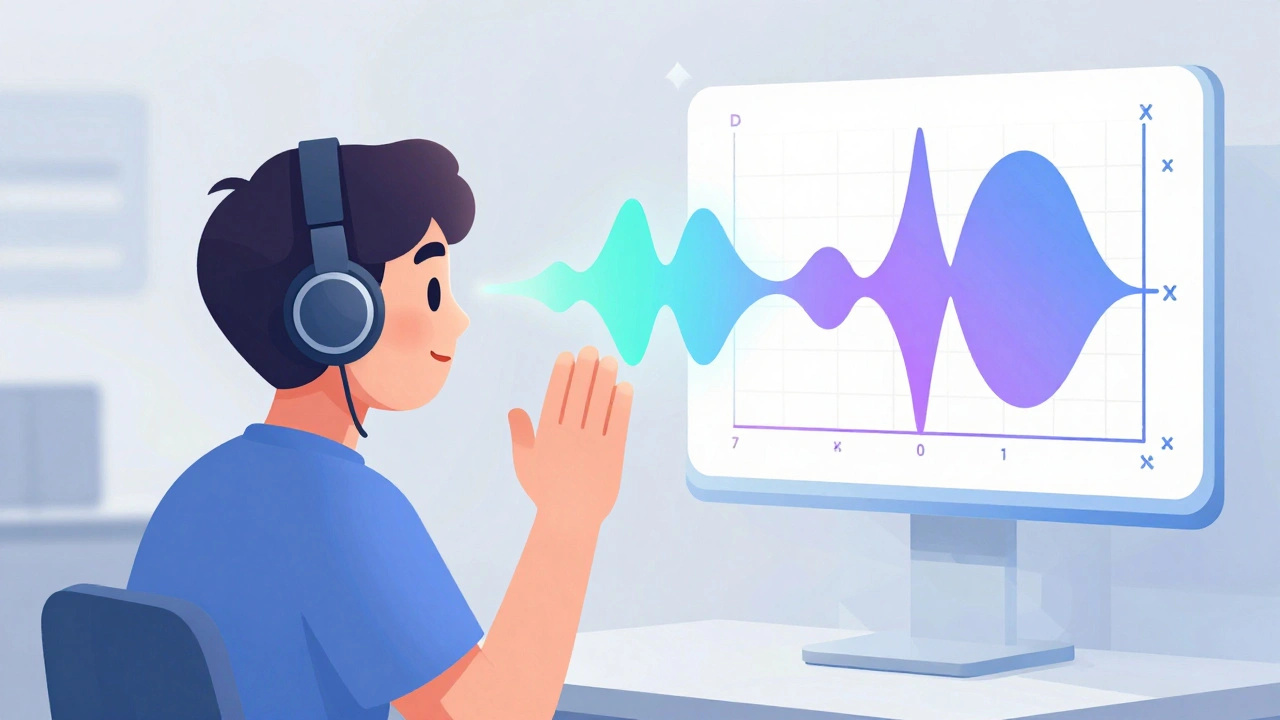
What happens during the test? You’ll wear headphones and press a button every time you hear a tone, even if it’s faint. The results are plotted on a graph called an audiogram, a visual record of your hearing sensitivity across different frequencies. This map shows exactly where your hearing dips—whether it’s high-pitched sounds like birds chirping or low tones like a bass drum. It also helps doctors tell if the problem is in your ear canal, middle ear, or inner ear. If your audiogram shows a pattern linked to noise exposure, aging, or medication side effects, you’ll know what’s going on and what steps to take next.
Some medications, like certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs, can damage hearing over time. That’s why audiometry testing is often part of routine monitoring for people on long-term treatments. It’s also used in workplaces with loud machinery to catch early signs of occupational hearing loss. Even if you think your hearing is fine, a baseline test at age 50 or after repeated loud exposures gives you a reference point for future checks. Hearing loss doesn’t always come with a warning—it creeps in slowly, and by the time you notice, it’s often harder to reverse.
There’s no pain, no needles, and no preparation needed. You just sit, listen, and respond. But the value? It’s huge. Catching hearing loss early means you can use hearing aids sooner, protect your remaining hearing, and avoid the social isolation and cognitive decline linked to untreated hearing problems. This collection of posts dives into real cases where hearing tests uncovered hidden issues, how to interpret your audiogram, what to ask your audiologist, and which medications might be silently hurting your ears. You’ll find practical advice from people who’ve been there—and the science behind why ignoring a quiet ear isn’t an option.
 9 Dec
9 Dec
Audiometry Testing: Understanding Hearing Assessment and Decibel Levels
Audiometry testing measures hearing sensitivity using decibel levels across frequencies to detect hearing loss. Learn how pure-tone and speech tests work, what audiograms reveal, and why early assessment matters for clear communication and treatment.
Read More...