QR Code Accessibility Checker
Access Score: 0%
Your ability to access drug safety information via QR codes.
Based on the article: 63% of patients and pharmacy staff know about QR codes, but 60% of elderly patients in rural clinics can't access information due to technology barriers.
Imagine a world where a simple scan of your medication's QR codes on drug labels instantly updates you about a critical safety warning-no waiting months for a new label. That's the reality today for millions of patients thanks to QR codes on drug labels. This technology shifts pharmaceutical labeling from static print to dynamic digital content, ensuring patients and healthcare providers always have the latest safety information. Let's explore how this innovation works, its benefits, challenges, and what's next.
How QR Codes on Drug Labels Work
QR codes on drug labels link to secure digital content hosted in the cloud. Unlike traditional printed labels, these codes use dynamic technology that allows updates without changing the physical label. When scanned, they provide access to real-time information like dosage instructions, side effects, and safety alerts.
Pharmaceutical companies use specialized systems like DosePacker's CareCommunityOS platform to manage this content. These systems integrate with pharmacovigilance databases, so safety updates can be pushed globally within 90 days. This is a massive improvement over the old process, which could take years to update labels across different countries.
The QR codes must meet specific standards: they're large enough to scan easily, positioned clearly on the packaging, and tested across various devices. Security measures like encryption ensure the information is authentic and can't be tampered with. For example, sQR.me provides tools to verify QR code scannability across Android, iOS, and older phone models.
Why This Matters for Patient Safety
Medication errors kill thousands each year. QR codes directly address this by providing accurate, up-to-date information. For example, when the FDA issues a black box warning-a critical safety alert-static labels can't change quickly. But with QR codes, the warning appears instantly when scanned. According to industry studies, 225 black box warnings were issued globally in a single decade, and QR codes help ensure patients get these updates immediately.
A Freyr Solutions case study showed emergency responders using QR codes to retrieve vital medication details during crises. Pharmacists also report fewer errors when using QR-linked electronic Patient Information Leaflets (ePILs) to counsel patients. In a 2024 PMC study, pharmacy staff said they'd use ePILs to improve patient communication, aligning with Good Pharmacy Practice Guidelines.

The Challenges We Can't Ignore
Despite the benefits, QR codes have real limitations. Not everyone has a smartphone or internet access. A 2024 survey found 63% of patients and pharmacy staff knew about QR codes, but many elderly or rural patients struggle to use them. On Reddit, 'HospitalPharm2020' noted a 40% improvement in comprehension after implementing QR codes, but 'MedTechWatcher' reported 60% of elderly patients in rural clinics couldn't access the information.
Privacy is another concern. GDPR and HIPAA regulations require strict data handling for scanned information. If a QR code links to a server in an unsecured location, patient data could be at risk. Some experts, like Dr. Maria Sanchez of the Global Health Institute, warn that QR codes risk creating a 'two-tier system' where those without digital access get inferior safety information.
Where QR Codes Are Taking Off Globally
Spain pioneered this technology in 2021 under regulatory approval. The UK followed in 2024 when the Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (ABPI) updated its Code of Practice to allow QR codes for promotional materials under Clause 12. Military pharmacies in the US started using them in 2022 to replace printed drug info.
Europe leads adoption, but Asian and African markets face infrastructure challenges. The European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) is working on a unified regulatory framework for QR codes across Europe, which will likely accelerate adoption. Meanwhile, companies like Vodori and Freyr Solutions are helping pharmaceutical firms navigate these regional differences.
What's Next for QR Code Safety Updates
The future looks bright. By 2025, regulators are expected to mandate QR codes for dynamic content, enabling real-time updates within 90 days of approval. Integrating AI could detect safety signals faster, while platforms like DosePacker's MyDoses app connect QR codes to medication management tools.
Global pharmacovigilance networks will expand, sharing data across borders to improve drug safety. However, success depends on solving digital equity issues. Experts recommend hybrid approaches-keeping printed instructions alongside QR codes-to ensure no one is left behind.
Practical Steps for Patients and Pharmacies
Patients: Scan the QR code with your phone camera or a free app. Ensure you're on a secure connection. If the scan fails, ask your pharmacist for help. Pharmacies can support patients by offering scanning assistance and clear printed instructions.
Pharmacies: Work with technology partners like DosePacker to integrate QR codes into dispensing systems. Train staff on troubleshooting common issues. Always have backup printed materials for patients who can't access digital content.
Regulators and manufacturers must collaborate to standardize QR code formats globally. This ensures consistent safety information regardless of location.
| Feature | QR Code System | Traditional Printed Labels |
|---|---|---|
| Update Speed | Real-time (within hours) | Months to years |
| Accessibility | Requires smartphone and internet | Always available |
| Accuracy | Always current | Outdated after updates |
| Security | Encrypted, anti-counterfeit | Vulnerable to counterfeiting |
How do QR codes on drug labels improve safety?
QR codes link to secure digital content that updates instantly when new safety information is available. Unlike printed labels, which become outdated immediately after regulatory changes, QR codes provide real-time access to critical updates like black box warnings. For example, when a medication's dosage instructions change due to new research, the QR code directs users to the latest version within hours. This reduces medication errors caused by outdated information.
Can I trust the information from a QR code scan?
Yes, when implemented correctly. Pharmaceutical companies use encrypted QR codes that link directly to manufacturer-controlled servers. Each scan creates an audit trail showing the version of information accessed. For example, DosePacker systems verify content authenticity using digital signatures. Regulatory bodies like the ABPI require these security measures to prevent counterfeiting or tampering.
What if my smartphone can't scan the QR code?
Many pharmacies offer free scanning assistance at the counter. If you're in a rural area with limited connectivity, ask for printed instructions alongside the QR code. The ABPI's 2024 guidelines require all QR code implementations to include backup printed safety information. For older phones, try using a dedicated QR scanner app like QR Code Reader (free on Android/iOS) which works better than camera apps in low-light conditions.
Are QR codes mandatory on all drug labels?
Not yet. Spain was the first to mandate QR codes for certain medications in 2021. The UK allows them under voluntary guidelines but doesn't require them. In the US, military pharmacies use QR codes, but civilian pharmacies aren't mandated. Regulatory bodies like the EFPIA are working toward global standards, with a target of full adoption by 2028. However, all new drug approvals since 2023 include QR code options in the labeling process.
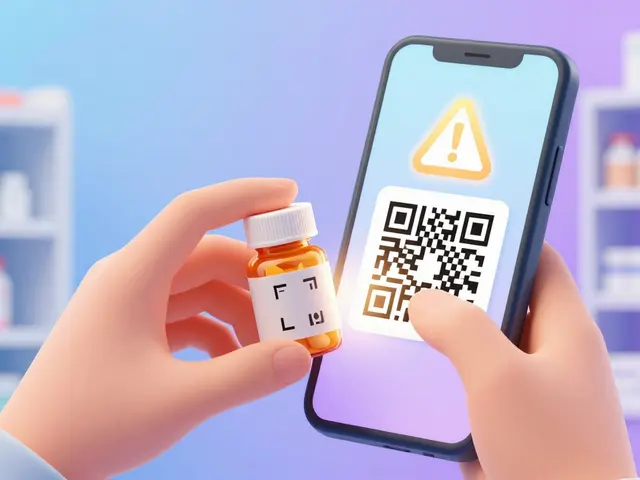
How do QR codes help prevent counterfeit drugs?
Each QR code contains a unique identifier that links to the drug's manufacturing batch details. Scanning it verifies authenticity against the manufacturer's database. For example, sQR.me systems check lot numbers and expiration dates against global supply chain records. Counterfeit drugs often have fake or missing QR codes, making them easier to identify. In 2024, this feature helped intercept over 200,000 fake medication packages in Europe alone.







Phoebe Norman
February 6, 2026 AT 13:28