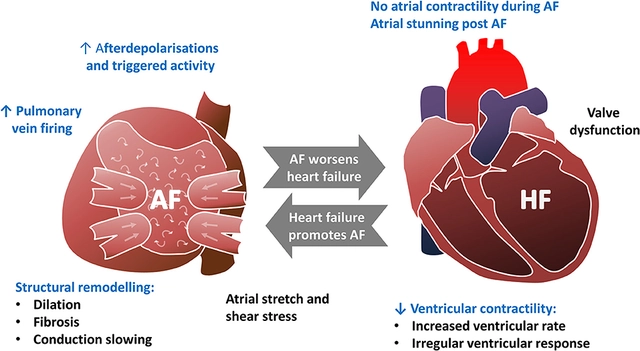
The Potential Role of Rivaroxaban in Treating Heart Failure
May 11 2023Insomnia – Understanding the Nighttime Struggle
When dealing with Insomnia, a frequent sleep disorder that makes falling or staying asleep difficult. Also known as sleep disorder, it can affect anyone from busy parents to shift workers. Common ways to tackle it include over‑the‑counter sleep aids, medications like diphenhydramine or doxylamine that promote drowsiness, natural supplements such as melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep‑wake cycle, and behavioral programs like CBT‑I, cognitive‑behavioral therapy for insomnia that reshapes thoughts and habits around sleep. Understanding how these pieces fit together helps you choose the right approach.
Why does insomnia happen? Stress, caffeine, irregular schedules, and underlying medical issues all play a part. People with anxiety often lie awake because their mind keeps replaying worries, while those with depression may experience fragmented sleep. Hormonal shifts during menopause or hyperthyroidism can also disturb your night. Recognizing the root cause lets you target treatment more precisely, whether that means adjusting your diet, managing a health condition, or tweaking your bedtime routine.
Key Approaches to Manage Insomnia
First, try improving sleep hygiene. Keep the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet; limit screen time an hour before bed; and stick to a consistent wake‑up time, even on weekends. These simple steps often reduce the need for medication. If lifestyle tweaks aren’t enough, consider short‑term OTC sleep aids, such as Unisom (diphenhydramine) or doxylamine, which many people find helpful for occasional sleeplessness. However, they can cause morning grogginess, so use them sparingly.
For chronic cases, prescription options like zolpidem or eszopiclone may be appropriate, but they require a doctor's oversight due to potential dependence. In parallel, many users benefit from melatonin supplements taken 30‑60 minutes before bedtime; the dosage typically ranges from 0.5 mg to 5 mg, depending on age and sensitivity. Research shows melatonin can shorten the time it takes to fall asleep, especially for shift workers or travelers dealing with jet lag.
Behavioral therapy, specifically CBT‑I, tackles the mental side of insomnia. It teaches you to challenge nighttime worries, set a realistic sleep window, and use relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery. A typical program runs for 6‑8 weeks and often yields lasting improvements without medication. Combining CBT‑I with short‑term sleep aids can speed up progress, but the therapy alone is powerful enough for many.
Sometimes other health problems hide behind sleeplessness. Chronic pain, restless‑leg syndrome, and sleep apnea each require targeted treatment. If you snore loudly, feel gasping during the night, or wake up with a dry mouth, a sleep study might uncover apnea, which is treated with CPAP machines or oral appliances. Addressing these conditions often resolves insomnia without any sleep‑inducing drugs.
Nutrition and exercise also matter. Heavy meals, alcohol, or caffeine close to bedtime can disrupt the natural sleep cycle. Regular physical activity—ideally earlier in the day—boosts sleep quality, but intense workouts right before bed may keep you alert. Hydration is key, too; staying hydrated prevents nighttime awakenings, but limit fluids an hour before sleep to avoid bathroom trips.
Finally, keep track of what works. A simple sleep diary records bedtime, wake time, any naps, caffeine or alcohol intake, and how you feel each morning. Over a couple of weeks, patterns emerge, helping you fine‑tune the combination of hygiene, supplements, and possibly therapy that suits you best.
Below you’ll find a curated selection of articles that dive deeper into specific sleep‑aid comparisons, lifestyle tweaks, and medical insights—all aimed at giving you practical steps to reclaim restful nights.
 12 Oct
12 Oct
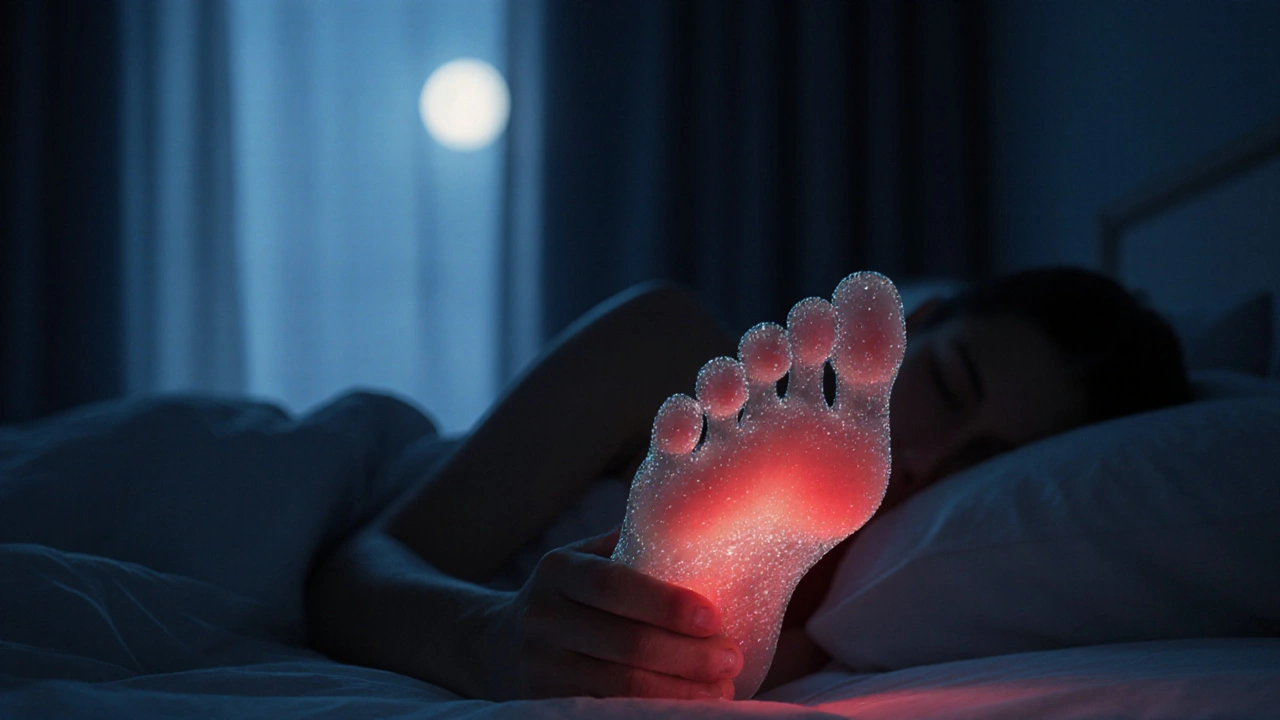
Gout and Sleep: How Gout Impacts Your Sleep Quality
Discover why gout attacks often break your sleep, learn practical tips to ease nighttime pain, and know when medical help is needed for better rest.
Read More...