Understanding Hirsutism and Its Causes
Hirsutism is a condition characterized by excessive hair growth in women, typically in areas where hair growth is usually minimal or absent. This can include the face, chest, back, and inner thighs. Hirsutism can be caused by several factors, including genetics, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. One of the most common causes of hirsutism is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), which affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Explained
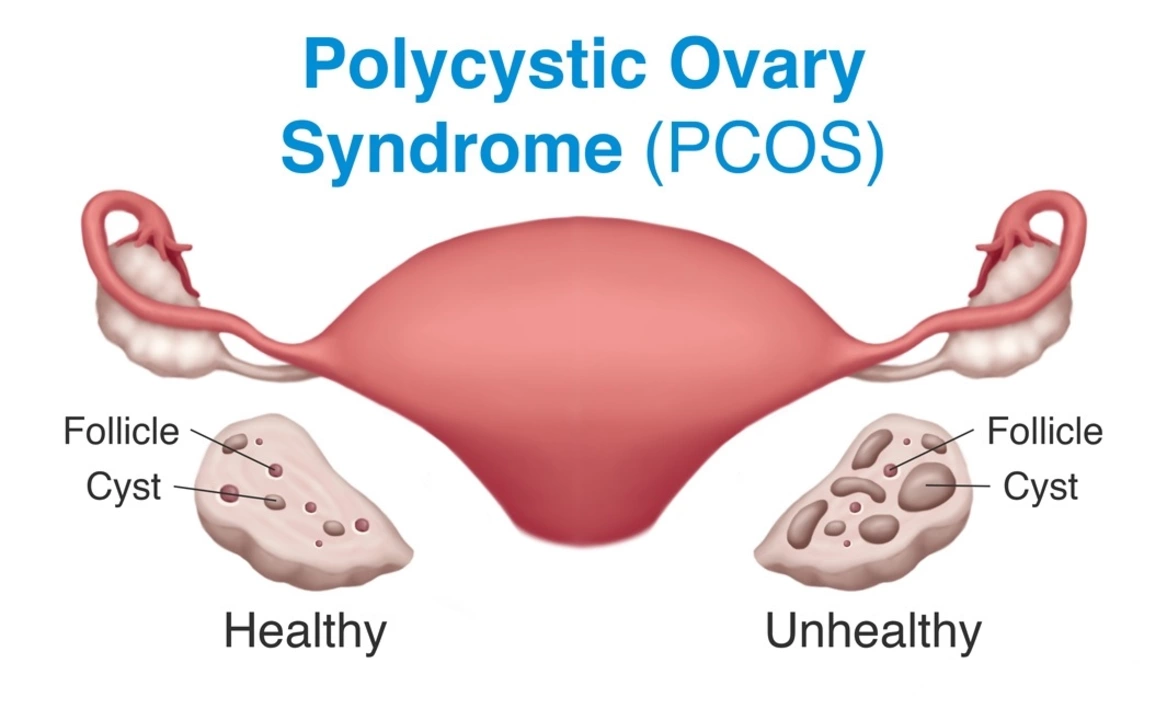
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or PCOS, is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts in the ovaries, which can lead to hormonal imbalances. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it is thought to be related to insulin resistance and inflammation. Some of the common symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, acne, and weight gain. In addition to causing hirsutism, PCOS can also lead to other health complications such as infertility, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
The Role of Hormones in Hirsutism and PCOS
Hormonal imbalances play a significant role in the development of both hirsutism and PCOS. In women with PCOS, the ovaries produce an excess of androgens, which are male hormones. These elevated androgen levels can lead to unwanted hair growth, acne, and other symptoms of hirsutism. Insulin resistance, a common feature of PCOS, can also contribute to increased androgen production. Furthermore, the hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods and, in some cases, infertility.
Diagnosing Hirsutism and PCOS
Diagnosing hirsutism involves a thorough evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and laboratory testing. A healthcare provider may assess the pattern and severity of hair growth using the Ferriman-Gallwey scoring system. In addition to evaluating for hirsutism, healthcare providers will also screen for underlying conditions that may be contributing to the excessive hair growth. This includes testing for hormonal imbalances and assessing for the presence of PCOS. Diagnosing PCOS typically involves ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms and may include ultrasound imaging of the ovaries to detect the presence of multiple cysts.
Treatment Options for Hirsutism and PCOS
There are various treatment options available for managing hirsutism and PCOS. For hirsutism, treatment typically focuses on addressing the underlying cause, such as hormonal imbalances, and may include medications that block the production of androgens or reduce their effects on hair follicles. In addition to medications, hair removal techniques such as electrolysis or laser hair removal can help manage the cosmetic aspects of hirsutism. For PCOS, treatment often involves lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity, to help improve insulin resistance and manage symptoms. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to regulate hormones, manage insulin resistance, or address specific symptoms such as acne or infertility.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hirsutism and PCOS
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing both hirsutism and PCOS. This includes making changes to your diet, incorporating regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. A balanced diet that focuses on whole foods, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can help improve insulin resistance, regulate hormones, and reduce inflammation. Regular physical activity is also essential, as it can help improve insulin sensitivity, manage weight, and promote overall health. In addition to diet and exercise, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can also be beneficial in managing the symptoms of both hirsutism and PCOS.
Alternative Treatment Options for Hirsutism and PCOS
In addition to conventional medical treatments and lifestyle changes, there are alternative treatment options available that may help manage the symptoms of hirsutism and PCOS. These may include herbal supplements, acupuncture, or other complementary therapies. While there is limited scientific evidence to support the efficacy of these treatments, some women find them helpful in managing their symptoms. It is essential to discuss any alternative treatments with your healthcare provider before beginning, as some supplements or therapies may interact with medications or have potential side effects.
The Emotional Impact of Hirsutism and PCOS
It's essential to recognize that hirsutism and PCOS can have a significant emotional impact on women who are affected. The physical symptoms of both conditions, such as excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain, can negatively affect self-esteem and body image. Furthermore, the potential for fertility issues associated with PCOS can cause additional emotional distress. It is crucial for women experiencing these emotional challenges to seek support from friends, family, or a mental health professional. Support groups specifically designed for women with hirsutism or PCOS can also provide valuable resources and a sense of community.
Conclusion: Navigating the Connection between Hirsutism and PCOS
Understanding the connection between hirsutism and PCOS is vital for women who are experiencing symptoms of excessive hair growth or other indications of hormonal imbalances. By recognizing the potential underlying causes of hirsutism, such as PCOS, women can work with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of these conditions. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and support, women with hirsutism and PCOS can manage their symptoms and live healthy, confident lives.





cris wasala
May 17, 2023 AT 04:00