Introduction to Overactive Bladder and Neurological Disorders
Many people may not realize the connection between overactive bladder (OAB) and neurological disorders. As someone who has experienced the challenges of an overactive bladder, I've found it essential to understand this link in order to better manage my symptoms and seek the right treatment. In this article, we will explore the relationship between OAB and neurological disorders, as well as discuss various treatment options available for those affected by these conditions.
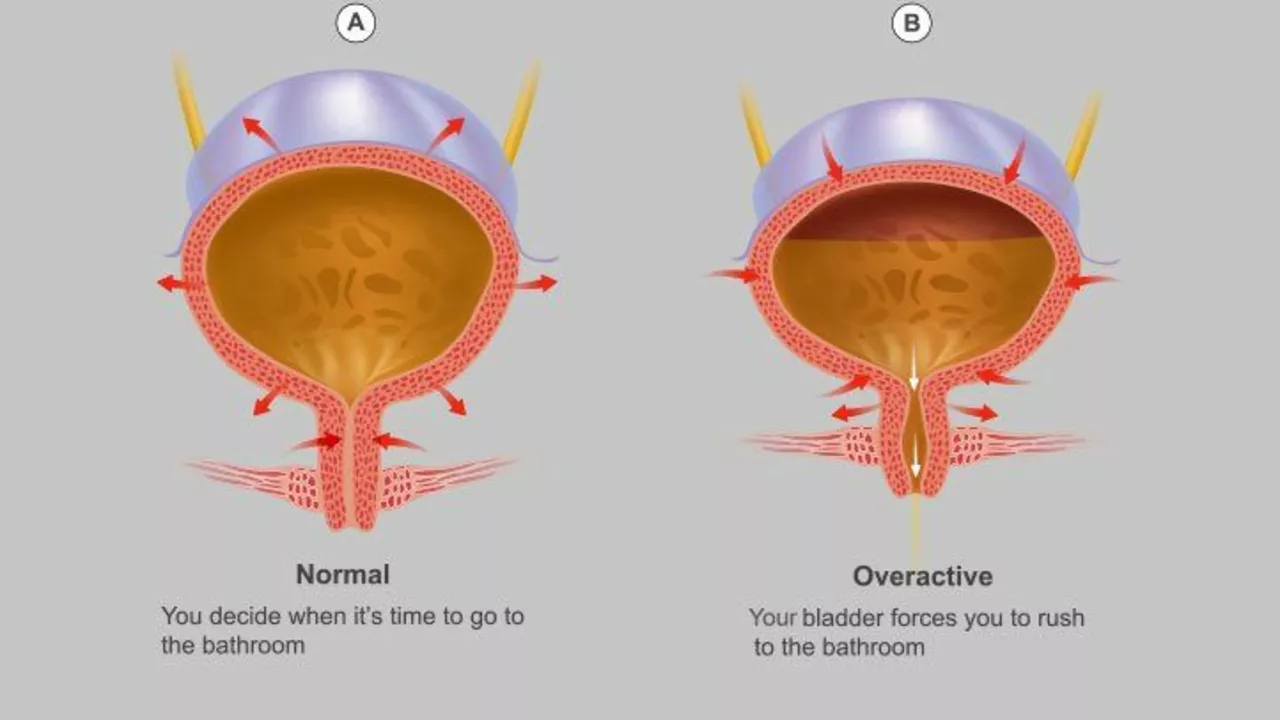
What is Overactive Bladder?
Overactive bladder is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate, and can result in frequent trips to the bathroom, often with little warning. This can greatly impact a person's quality of life, causing embarrassment, anxiety, and even sleep disturbances. OAB can be caused by various factors, such as aging, hormonal changes, and certain medications. However, there is also a strong link between OAB and neurological disorders, which we will explore in the following sections.
Neurological Disorders and Overactive Bladder
Neurological disorders are conditions that affect the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body. These disorders can have a significant impact on bladder function, as the nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling the muscles that regulate urination. Some common neurological disorders that can contribute to OAB include multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and stroke.
Multiple Sclerosis and Overactive Bladder
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the central nervous system, causing a wide range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. One common symptom of MS is bladder dysfunction, including overactive bladder. In fact, up to 80% of people with MS experience some form of bladder problems. This is because the damage to the nerves in the central nervous system can disrupt the signals that control bladder function, leading to OAB and other urinary issues.
Parkinson's Disease and Overactive Bladder
Parkinson's disease is another neurological disorder that can contribute to overactive bladder symptoms. This progressive disorder affects the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine, which is essential for smooth and coordinated muscle movements. As Parkinson's disease progresses, it can cause problems with bladder control, leading to OAB symptoms such as urgency, frequency, and incontinence.
Stroke and Overactive Bladder
Stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, either by a blood clot or a burst blood vessel. This disruption in blood flow can cause damage to the brain, which can then lead to various neurological symptoms, including bladder dysfunction. Up to 50% of stroke survivors experience urinary issues, including overactive bladder, as a result of the damage to the nerves that control bladder function.
Diagnosing the Cause of Overactive Bladder
If you suspect that your overactive bladder symptoms may be related to a neurological disorder, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They will likely perform a comprehensive evaluation, which may include a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and various tests to determine the underlying cause of your OAB symptoms. By identifying the specific neurological disorder, your healthcare provider can then develop an appropriate treatment plan to help manage your overactive bladder.
Treatment Options for Overactive Bladder and Neurological Disorders
There are several treatment options available for managing overactive bladder symptoms related to neurological disorders. These may include medications, lifestyle changes, and even surgical interventions. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of your symptoms, as well as the underlying neurological condition. Some possible treatment options include:
Medications
Anticholinergic medications are often prescribed to help relax the bladder muscles and decrease the frequency and urgency of urination. Additionally, medications that target the specific neurological disorder, such as disease-modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis or dopamine replacement therapy for Parkinson's disease, may also help improve bladder function.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage overactive bladder symptoms. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, participating in regular physical activity, and avoiding bladder irritants such as caffeine and alcohol. Additionally, practicing bladder training techniques, such as scheduled voiding and pelvic floor exercises, can help improve bladder control.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered if other treatment options have not been successful in managing overactive bladder symptoms. This may include procedures such as sacral nerve stimulation, which involves implanting a small device to stimulate the nerves that control bladder function, or botulinum toxin injections, which can help relax the bladder muscles and reduce symptoms of OAB.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between overactive bladder and neurological disorders is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. If you are experiencing OAB symptoms and suspect a neurological condition may be the cause, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. By addressing the specific neurological disorder, you can improve your bladder function and overall quality of life.





Georgia Nightingale
May 14, 2023 AT 14:22